
What is the Stock Exchange and how does it work?
If you are a new to the stock market you might be wondering how the stock exchange works and what is it. Well, a stock exchange is a place where stocks are traded.
A stock exchange is basically a marketplace where participants meet to buy and sell shares of stock. It provides a single, neutral location for everyone to come together to execute trades.
An exchange is actually an institution or organization which hosts a market where stocks are traded, such as the NYSE or NASDAQ.
If you have ever watched the opening bell being rung at the NYSE you have witnessed the opening of the day’s trading on an exchange and on a trading floor. This is an example of a exchange with a real location, with real stock traders yelling and screaming on the trading floor to place trades.
There are also other types of stock exchanges which are virtual, which mean it doesn’t have an actual trading floor. These virtual or electronic stock exchanges, such as the NASDAQ, are made up of a network of computers where the stock trades are executed electronically.
In today’s market, just about all trading occurs electronically across a number of different stock exchanges. The stock exchanges facilitate the matching of buyers and sellers in order to execute trades.
The purpose of a stock exchange is to facilitate the exchange of securities between buyers and sellers, thus providing a marketplace. Stock prices are simply established through supply and demand. A dedicated network of traders, brokers, and specialists ensures that buy and sell orders are executed in a timely and professional manner.
The exchanges provide real-time trading information on the listed stock. Exchanges impose rules and regulations on the firms and brokers that are involved with them. If a particular company is traded on an exchange, it is referred to as “listed”.
In the United States, a company will most likely have their stock listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or the NASDAQ, which are the biggest and the most commonly used stock exchanges in the USA.
Companies that are not listed on a stock exchange are traded on the OTC (Over-The-Counter). Companies that have shares traded on the OTC are usually smaller and riskier because they do not meet the requirements to be listed on a stock exchange.
How the Stock Exchanges and the overall Stock Market Comes Together
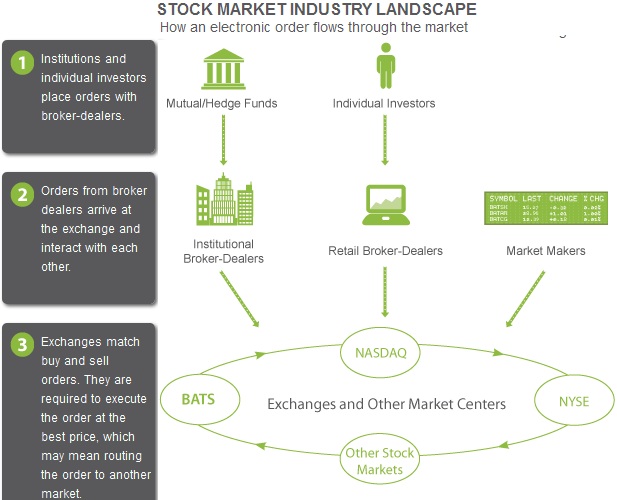
List of Stock Exchanges
Major Stock Exchanges in the United States
 The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE)
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE)
The New York Stock Exchange, commonly referred to as NYSE is the largest stock exchange in the world by market capitalization. The parent company of the New York Stock Exchange is now called NYSE Euronext, following a merger with the European exchange in 2007.
For many years, the NYSE was mainly done face-to-face on the trading floor. Today, the NYSE offers a hybrid model, with a floor-based marketplace and an electronic one. More than half of all NYSE trades are conducted electronically, although floor traders are still used to set pricing and deal in high volume institutional trading.
There are over 3,000 listed companies trading on the NYSE. Some of the largest companies in America are listed on the NYSE such as Walmart, Coca-Cola, McDonalds and among others.
 NASDAQ
NASDAQ
The NASDAQ is the second-largest stock exchange by market capitalization in the world, after the New York Stock Exchange. All stock trades are done electronically and the NASDAQ has more trading volume than any other electronic stock exchange in the world.
The NASDAQ is a huge exchange, there are over 2,700 companies listed on the NASDAQ, that range from small-cap to large-cap stocks. Many tech giants are listed on the NASDAQ such as: Apple, Microsoft, Intel, Dell and many others.
 AMEX
AMEX
The American Stock Exchange, now known as NYSE Amex Equities after the NYSE Euronext acquired it in 2008. It is the third-largest stock exchange by trading volume in the United States.
The AMEX features mostly small and micro cap companies. It is a great place to find some of the next emerging businesses.
 BATS Global Markets
BATS Global Markets
When BATS launched in 2005, it was an alternative trading system (ATS), which also referred to as Alternative Trading Networks or an Electronic Communication Network (ECN).
However, in 2008, it transitioned from an ATS to a registered national U.S. stock exchange that competes with the New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ. BATS Global Markets is now a stock exchange where companies can be listed and has become the third-largest in the United States by volume.
BATS operates two stock exchanges in the U.S., the BZX Exchange and the BYX Exchange (The BATS Exchanges), which currently account for about 10-12% of all U.S. equity trading on a daily basis.
Over-The-Counter (OTC) and Pink Sheets
This is not really an exchange, but rather it is where companies trade that are not listed on a stock exchange. Companies that trade on the OTC are usually smaller and often referred to penny stocks. Stocks that trade on the OTC are considered riskier because they do not meet the requirements to be listed on a stock exchange.
There are two different markets for stocks that trade Over-The-Counter: The OTC Bulletin Board (OTCBB) and OTC Markets (formerly Pink Sheets)![]() OTC Markets (formerly Pink Sheets)
OTC Markets (formerly Pink Sheets)
The OTC Markets is not a stock exchange, but rather the company facilitates the exchange of securities between qualified independent brokers. Here you can find a variety of penny stocks, many of which are usually thinly traded microcap companies.
This market is divided into 3 tiers:
- The OTCQB is for companies registered with the SEC
- The OTCQX is for companies who aren’t registered with the SEC but do report their audited financials to the OTC Markets.
- The OTC Pink Markets is for companies who may or may not disclose any information to the public. These are the most speculative of the three tiers.
![]() OTC Bulletin Board (OTCBB)
OTC Bulletin Board (OTCBB)
The OTC Bulletin Board (OTCBB) is a regulated quotation service that displays real-time quotes, last-sale prices, and volume information in over-the-counter (OTC) equity securities. An OTC equity security generally is any equity that is not listed or traded on NASDAQ or a national securities exchange. Broker-dealers who subscribe to the system can use the OTCBB to look up prices or enter quotes for OTC securities.
The OTCBB features a variety of penny stocks, many trading between $0.01 & $1 per share and are usually thinly traded microcap companies.
The OTCBB has the following features:
- provides access to more than 3,500 securities
- includes more than 300 participating Market Makers
- electronically transmits real-time quote, price, and volume information
- displays indications of interest and prior-day trading activity
Other Major Stock Exchanges around the world
Japan – Tokyo Stock Exchange
United Kingdom – London Stock Exchange
China – Shanghai Stock Exchange
China – Hong Kong Stock Exchange
Canada – Toronto Stock Exchange
Brazil – BM&F Bovespa
Australia – Australian Securities Exchange
Germany – Deutsche Börse



